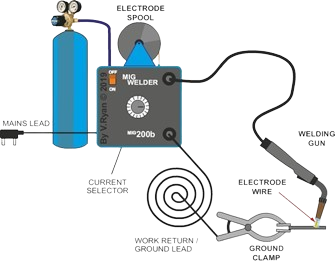
What is MIG?
Metal Inert Gas (MIG), also commonly known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is a popular and versatile welding process used to join metals. In MIG welding, a continuous and consumable electrode is fed through a welding torch/gun, while a shielding gas is simultaneously emitted to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. The welding machine controls the wire feeder speed and the gas flow, making the process semi-automatic or automatic, depending on the setup.
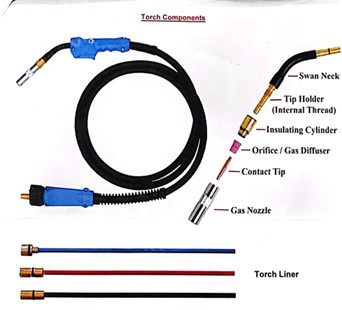
What is MIG Torch?
MIG torch, also known as MIG gun or welding gun, is a crucial tool that empowers welders to create strong, precise, and efficient welds. An MIG torch consists of several key components, each serving a specific function in the welding process. Let’s explore these essential elements:
- Swan Neck: It is the curved part of the welding torch which connects the handle to the torch’s main body. Its design enables welders to access tight spaces and challenging angles with ease.
- Tip Holder: The tip holder is a crucial component that securely holds the contact tip, which allows for a stable welding arc and consistent welds.
- Insulating Cylinder: Prevents electrical current from travelling along the torch’s This keeps the focus on the contact tip and enables them to control their welds better.
- Orifice: The orifice, also known as gas diffuser, directs the flow of shielding gas around the welding wire and weld pool, resulting in clean and durable welds.
- Contact Tip: The contact tip is the point of contact between the welding torch/gun and the welding wire as it transfers the welding current to the Choosing the right size of contact tip is essential for smooth welding operations.
- Gas Nozzle: The gas nozzle directs the gas flow to shield the weld pool. It also influences the shape and size of the weld bead, contributing to the visual appearance of the final weld.
- Torch Liner: A well-maintained and appropriate sized torch liner ensures an uninterrupted wire feed. This minimises the risk of weld defects and ensures smoother welding operations.
Pros & Cons of Choosing MIG Welding
MIG welding offers several advantages including its versatility to weld a wide range of metals, efficiency, ease of use, and environmental safety. However, common known disadvantages include limited welding positions, outdoor limitations, possible necessity to preheat thicker metals, and high cost.
PROS |
CONS |
|
VERSATILITY Can be used on a wide range of metals: – Stainless Steel, Mild Steel, and Aluminium |
NOT IDEAL FOR ALL POSITIONS Best suited for flat and horizontal welding positions. Vertical and overhead position may be more of a challenge. |
|
HIGH WELDING SPEED Relatively fast therefore ideal for projects that require efficiency and productivity. |
OUTDOOR LIMITATIONS Wind can reduce the effectiveness of the machine and affect the weld quality. |
|
EASE OF USE Semi-automatic or automatic processes create an ease of use. |
THICKER METALS REQUIRE PREHEATING Preheating may be necessary on thicker metals to prevent cracking. |
|
REDUCED WELDING FUMES Lesser welding fumes are produced, enhancing comfort and environmental safety. |
COMPLEX & COSTLY MIG welding can be more complex and expensive, especially when incorporating advanced features or automation. |
|
|
Conclusion
Understanding MIG welding and its torch components unlocks the door to precision and efficiency in a welder’s welding journey. It is a powerful welding process that offers versatility, speed, and cleaner welds. However, like any other welding process, MIG welding has its pros and cons, making it essential to consider your project’s specific needs.
DANOX MIG500I SEPARATE FEEDER WELDING MACHINE
✓ High welding efficiency
✓ Optimised performance with adjustable inductance
✓ Comes with Wire Feeder unit




